Describe the Lytic Cycle of Virus Reproduction
However the mechanisms of penetration nucleic-acid biosynthesis and release differ between. The host cell bursts and releases new viruses.

The Viral Life Cycle Microbiology
Viruses capable of latency may initially cause an acute infection before becoming dormant.

. There are two main ways that viruses reproduce or multiply and these are listed below. There are viruses that are capable of remaining hidden or dormant inside the cell in a process called latency. No provirus is created.
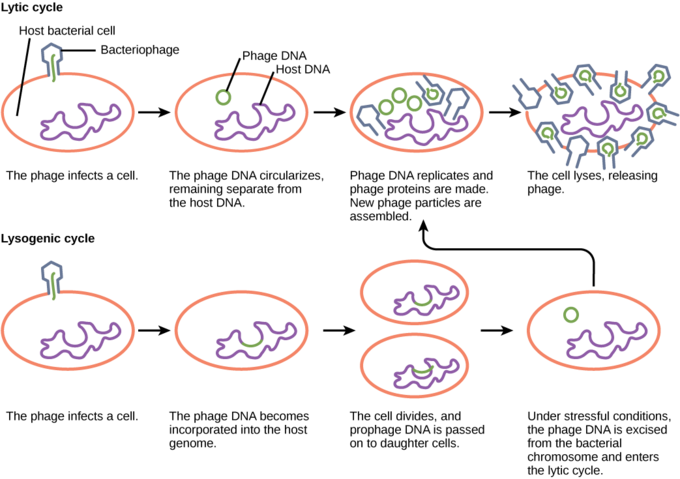
Viral reproduction takes place in two cycles viz the lysogenic and lytic cycle. Following are the steps of lytic cycle. The released λ-phages then infect new bacterium and continue another lytic cycle or may enter into a lysogenic cycle.
The following article is a discussion of the steps to help you understand this process. The lytic cycle is a replication process carried out by a virus within a bacterial cell. The lytic cycle is one of the two cycles of viral reproduction referring to bacterial viruses or bacteriologist the other being the lysogenic cycle.
These types of viruses are known as latent viruses and may cause latent infections. Life Cycle of Viruses with Animal Hosts. These are then assembled into new virus particles.
Release of new virus particles. In the video Virus Lytic Cycle a bacteriophage which is a virus that infects and replicates within a bacterium attaches itself and infects the host cell. The lysogenic cycle is a method by which a virus can replicate its DNA using a host cell.
Florianmanteyw and 3 more users found this answer helpful. The virus life cycle could be divided into six steps. The nucleus is omitted for clarity.
The lytic reproductive cycle takes place when the virus enters a cell and immediately overwrites its genetic material on it. Not all animal viruses undergo replication by the lytic cycle. The latter is thought to be the main method of viral replication as it results in.
That is it quickly and directly attacks the cells. Attachment penetration uncoating gene expression and replication assembly and release. The genetic material of the virus DNA or RNA instructs the cell to start making viral proteins and nucleic acids DNARNA 3.
Assembly of a new viruses. Generally the virus continues lytic cycle with a few numbers of infected cells but major portion enters into lysogenic relationship and continues the lysogenic cycle. Describe the replication process of animal viruses.
The host cell makes protein coat and genetic material for the virus. This process is advantageous to the virus too. Most viruses reproduce through a process called lytic infection.
The lysogenic cycle or the lytic cycle. A lytic cycle is one of the ways by which a virus reproduces itself and escapes from the cell. This is called lysis and provides the name of the lytic cycle.
This cycle of virus reproduction is. Not all animal viruses undergo replication by the lytic cycle. It is one of the cycles of a bacteriophage virus in which their is a master-slave relationship between the bacteriophage master and bacteria slave.
Newly formed virus particles are released from. The virus attaches itself to the host cell. With the lytic cycle the virus attaches itself to a host cell and infuses the cell with its nucleic acid.
The life cycle of virus. Typically viruses can undergo two types of DNA replication. Attachment penetration biosynthesis maturation and release see Figure 610.
During lytic infection a virus enters the host cell makes a copy of itself and causes the cell to burst or lyse. It takes the pieces of the membrane with it and they serve as an ID card for entering the new cell. Get 1-on-1 help from an expert tutor now.
Discover the definition of the lytic cycle why a. The viral proteins and nucleic acids are brought together to make new virus particles. Virus that remains in the body for a long period of time but only causes intermittent symptoms lysis bursting of a cell lytic cycle type of virus replication in which virions are released through lysis or bursting of the cell.
It is an enveloped virus with a negative sense RNA segmented genome that encodes for 11 viral genes. The lytic cycle results in the destruction of the infected cell and its membrane. This acid takes the host cell hostage and the virus begins to multiply with nucleic acid and its protein coat thus developing into new viruses.
Influenza A virus belongs to the family of Orthomyxoviridae. There are viruses that are capable of remaining hidden or dormant inside the cell in a process called latency. It is the reproduction of viral cells.
Simply mean bursting or rupturing cycle over and over again. Learn about its mechanism and the lytic pathway. The lytic cycle is considered the main method of virus reproduction.
In the lytic cycle the DNA is multiplied. Lysogenic cycle can happen after the lytic cycle whereas the viral DNA is still present but in a dormant state. The host cell puts the viruses together.
In the lysogenic cycle however the viruses insert themselves into the DNA of the cells of the host. The lytic cycle is one of the two cycles of viral reproduction referring to bacterial viruses or bacteriophages the other being the lysogenic cycle. Viruses capable of latency may initially cause an acute infection before becoming dormant.
This virus has evolved a number of mechanisms that enable it to invade host cells and subvert the host cell machinery for its own purpose that is for the sole production of more virus. This causes the host cell or cells to burst. In the lysogenic cycle the DNA is only replicated not translated into proteins.
Lytic animal viruses follow similar infection stages to bacteriophages. Bacteriophages that only use the lytic cycle are called virulent phages in contrast to temperate phages. 5 stages in a viruses life cycle.
Lytic cycle is active viral replication causing the host to feel viral symptoms. The lytic cycle results in the destruction of the infected cell and its membrane. Lytic Cycle.
In this step the bacteriophage attaches itself by its tail to the cell wall of. The viral capsid blue and genome brown are schematically drawn for the purpose of explanation. After the viruses exit they move to another cell enter it and start the cycle again.
If the dormant virus undergoes stress or is exposed to radiation the viral lysogenic cycle can turn into the. Lysogenic Cycle Definition. These types of viruses are known as latent viruses and may cause latent infections.

Understanding The Lytic Cycle What Are The Steps Technology Networks

The Viral Life Cycle Microbiology

How Does The Lytic Cycle Of Viral Reproduction Works Quora
21 2b The Lytic And Lysogenic Cycles Of Bacteriophages Biology Libretexts
Comments
Post a Comment